What is an absorption chiller? A comprehensive guide to the operation, benefits and challenges of thermal cooling systems

Introduction: Did you know that cooling can be done with heat?
Many people think that cooling systems only work with electricity and a compressor.
But the truth is that absorption chillers do cooling using heat, not electricity!
This technology has found widespread use not only in large industries, but also in smart buildings, power plants and units that have excess thermal energy.
- But how can a system produce cold with heat?
- What is the difference between an absorption chiller and a compression chiller?
- And why does maintaining absorption chillers require careful analysis of water and lithium bromide solution?
In this article, you will find the answers to these questions and many more.
What is an absorption chiller?
An absorption chiller is a cooling system that uses heat (such as steam, hot water or direct flame) to drive the refrigeration cycle instead of an electric compressor.
In this system, water is used as the refrigerant (coolant) and lithium bromide is used as the absorbent (absorbent).
This unique combination allows cooling without the need for high electricity consumption.
The difference between absorption chillers and compression chillers
Feature | Compression chiller | Absorption chiller |
Energy source | Electricity (compressor) | Heat (steam, hot water, gas) |
Refrigerant | Freons (R134a, R410A) | Water |
Absorbent/solvent | — | Lithium bromide |
Sound | High (due to compressor) | Very low |
Maintenance | Mechanically complex | Chemically sensitive |
Electricity consumption | Top | Very low (for pumps only) |
Key point:An absorption chiller is ideal for units that have excess heat energy (such as recycled steam).
How a lithium bromide-water absorption chiller works
Step 1: Evaporation of water in the evaporator (cold production)
- The pressure inside the system is reduced to 0.01 atmospheres.
- At this low pressure, water begins to boil at a temperature of about 4°C.
- This evaporation takes latent heat from the circulating water (related to the ventilation system) and cools it.

Absorption Chiller Evaporator — Cold Water Production Site for Air Conditioning Systems
Step 2: Water Vapor Absorption by Lithium Bromide
- The produced water vapor is transferred to the absorber.
- The concentrated lithium bromide solution absorbs the water vapor.
- This process keeps the pressure inside the evaporator low so that evaporation continues.
Step 3: Water Separation in the Generator (High Pressure Generation)
- The diluted solution (lithium bromide + water) is pumped to the generator.
- In the generator, by applying heat (steam or hot water), the water is separated from the solution and enters the condenser as high-pressure vapor.
Generator and condenser of an absorption chiller with heat pipes
Step 4: Return of water to the evaporator
- The water vapor in the condenser is condensed and converted into liquid.
- This liquid water automatically returns to the evaporator due to the pressure difference.
- The cycle is completed.
Physical structure of absorption chillers
Absorption chillers are made in two types:
1. Double-cylinder absorption chiller
- Lower cylinder: evaporator + absorber (very low pressure)
- Upper cylinder: generator + condenser (relatively higher pressure)
2. Single-cylinder absorption chiller
- All parts are located in one chamber, but are separated by internal walls.
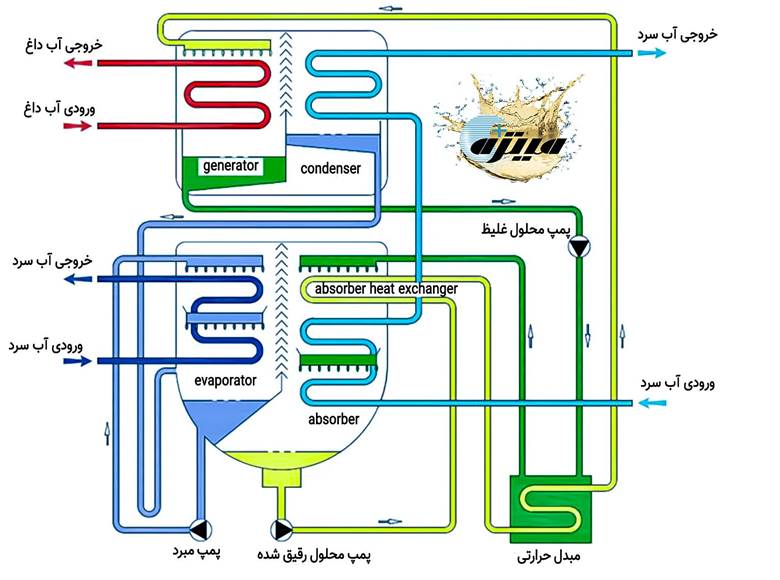
Single-effect absorption chiller
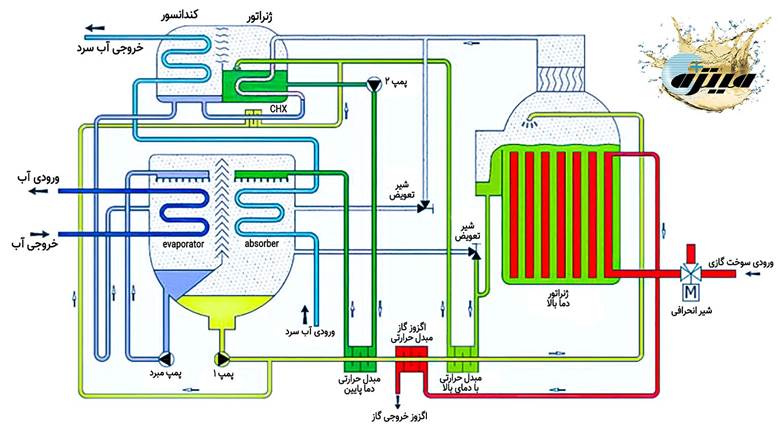
Double-effect absorption chiller
Why is absorption chiller maintenance challenging?
Absorption chillers are mechanically simpler than compression chillers, but they are chemically very sensitive.
1. Sensitivity to water quality
- Any mineral deposits (calcium carbonate, sulfate) in the evaporator or condenser create thermal insulation.
- This insulation reduces thermal efficiency by up to 30%.
2. Degradation of lithium bromide solution
- Lithium bromide can become corrosive in the presence of oxygen or high temperatures.
- This corrosion leads to leaks in the pipes and system failure.
3. Microbial contamination
- Proper humidity and temperature are ideal conditions for the growth of bacteria and algae in recirculating systems.
Common questions from users about absorption chillers
When should we use an absorption chiller?
- When you have excess steam or hot water (e.g. power plants, petrochemicals)
- When electricity costs are high
- When noise and vibration are prohibited (e.g. hospitals)
Is an absorption chiller less efficient?
Yes, the coefficient of performance (COP) of an absorption chiller (typically 0.7–1.0) is lower than that of a compression chiller (3–6).
But if you have free heat, the operating cost is much lower.
How to maintain an absorption chiller?
- Regular analysis of circulating system water
- Control of pH and TDS in the cooling circuit
- Monitoring of lithium bromide concentration
- Periodic descaling with safe chemical methods
Chemical challenges in absorption chillers and practical solutions
1. Scale formation in condenser and evaporator
- Cause: water hardness, high temperature
- Solution: use of scale inhibitors or chemical descaling
2. Corrosion in lithium bromide system
- Cause: presence of oxygen, improper pH
- Solution: use of corrosion inhibitors and control of the internal atmosphere
3. Reduction of lithium bromide concentration
- Cause: leakage, evaporation
- Solution: regular chemical analysis and solution replenishment
Conclusion:Absorption chiller, a smart solution for sustainable cooling
Absorption chillers are not just a cooling system — they are an energy recovery strategy.
By utilizing waste heat, you can:
- Reduce electricity consumption by up to 90%
- Optimize operating costs
- Reduce your carbon footprint
But the success of these systems depends entirely on careful chemical management.
Without regular analysis of water, lithium bromide solution, and sediments, even the best absorption chiller will suffer from reduced efficiency and failure.
Is the absorption chiller in your unit experiencing reduced efficiency, increased energy consumption, or corrosion?
Identify the root cause of the problem and receive a safe and effective solution by performing a comprehensive chemical analysis. (Contact Abrizan Laboratory)
share :












Submit your opinion
Your email address will not be published.