Types of deposits and corrosion in boilers + accurate detection methods

Misdiagnosis of the type of scale or corrosion in the boiler = Wrong choice of chemicals = Increased damage instead of reducing it
In this expert guide, we examine the types of common boiler scales (calcium carbonate, calcium sulfate, silica, iron oxide) and types of fatal corrosion (oxygen, subsedimentary, alkaline) in full detail. We also teach accurate diagnosis methods with advanced laboratory analysis (XRD, SEM, ICP) so that you can choose the best chemical solution for your system with high accuracy.
Why read this article?
✅ Identification of the 4 main types of boiler scales and their visual and chemical diagnosis
✅ Understanding the 3 types of fatal corrosion and how to diagnose each in the early stages
✅ Introduction to laboratory methods XRD, SEM, ICP and their application in detecting scale and corrosion
✅ Receive a quick diagnosis checklist for operators and engineers
✅ Introduction to specialized solutions for treating each type of scale and corrosion

Types of Boiler Scales — Diagnosis and Risks
Boiler scale is mainly caused by salts in the feed water. Here we will examine the 4 main types:
1. Calcium carbonate (CaCO₃)—the most common scale
- Source : Permanent water hardness (calcium + bicarbonate)
- Appearance : White or gray — brittle — chalk-like
Hazards:
- Reduced heat transfer → Increased metal temperature → Cracking
- Formation of insulating layer → Increased fuel consumption
Chemical detection:
- Solubility in dilute hydrochloric acid — with the formation of bubbles (CO₂)
- XRD analysis : Characteristic peaks of calcite
2. Calcium sulfate (CaSO₄)—Hardest deposit
- Origin : Sulfate + calcium in high TDS water
- Appearance : White or yellowish turbid — Very hard and sticky — Marble-like
Hazards:
- Strong adhesion to metal — Difficult to remove mechanically
- High resistance to common acids
Chemical identification:
- Insoluble in HCl — Partially soluble in hot HNO₃
- XRD analysis : Gypsum or Anhydrite peaks
3. Silica (SiO₂)—The most dangerous deposit
- Origin : Water-soluble silica — especially in groundwater and well water
- Appearance : Glassy or opaque — Very hard — Similar to glass glue
Hazards:
- Strong adhesion to metal and membranes — Inremovable with common acids
- Severe reduction in heat transfer — Even in thin layers
Chemical identification:
- Insolubility in mineral acids — Solubility in HF (dangerous!)
- SEM-EDS analysis : Identification of Si element — XRD analysis : Cristobalite or quartz peaks
4. Iron oxide (Fe₂O₃/ Fe₃O₄)—caused by corrosion
- Source : Corrosion of steel pipes or equipment — Iron in feed water
- Appearance : Dark red or black — Powdery or flaky — Rust-like
Hazards:
- Formation of insulating layer → Reduced heat transfer
- Intensified subsurface corrosion
Chemical identification:
- Solubility in HCl — Yellow-orange color of solution
- ICP analysis : High iron concentration — XRD analysis : Hematite or magnetite peaks

4 types of sediment from above: silica, iron oxide, calcium carbonate, calcium sulfate
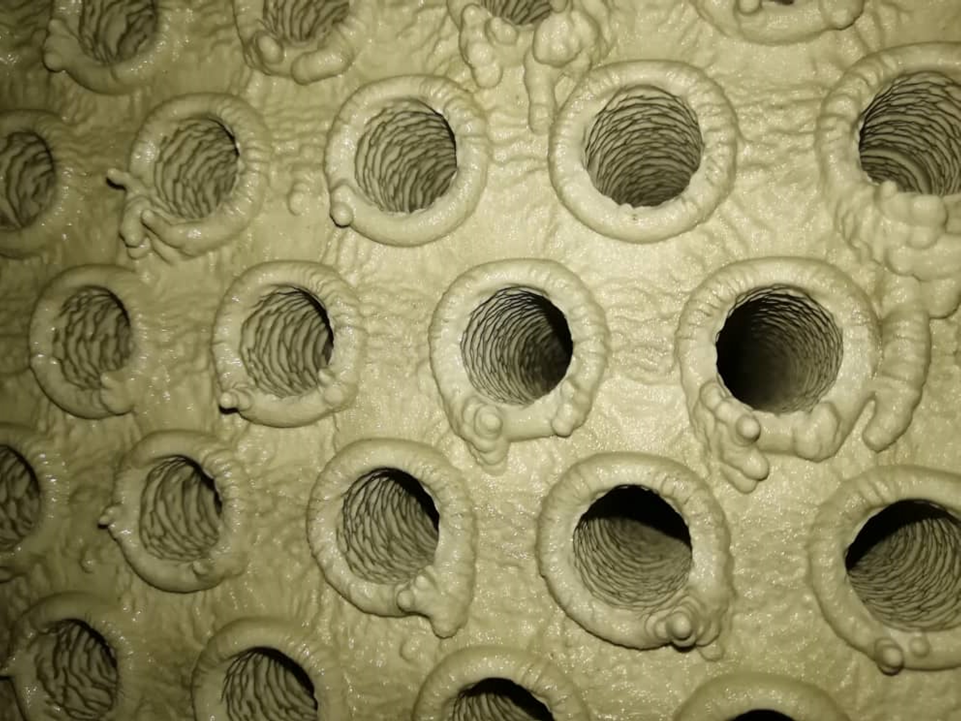
Deposits in water tube boilers

Deposits around the pipes in a fire tube boiler
Types of Boiler Corrosion — Diagnosis and Risks
Corrosion in boilers is often caused by poor feedwater quality or improper operation. Here we examine the 3 main types:
1. Oxygen Pitting Corrosion
- Source : Presence of dissolved oxygen in the feedwater — due to insufficient deoxygenation
- Appearance : Small, deep pits (pitting) — usually in the feedline, drum, and water pipes
Hazards:
- Rapid penetration into the metal thickness — Sudden rupture of the pipe
- Localized damage — Difficult to detect in the early stages
Diagnosis:
- Visual or endoscopic inspection — Circular pits with sharp edges
- SEM analysis: Cup-like shape of the pit — EDS analysis: Presence of O and Fe
2. Under-Deposit Corrosion
- Origin : Deposit formation on metal surface — creating a localized corrosive environment beneath the deposit
- Appearance : Localized corrosion beneath the deposit — usually with pitting or gouging
Hazards:
- Localized metal destruction — without warning
- Corrosion aggravated by the presence of chlorides or sulfides
Diagnosis:
- Inspection after deposit removal — localized corrosion beneath the deposit
- XRD/SEM analysis of the deposit and underlying metal — identification of corrosive compounds (⁻Cl⁻, S²)
3. Caustic Embrittlement / Alkaline Corrosion
- Source: Excessive alkali (⁻OH) concentration under the deposit or in cracks—usually at pH > 10.5
- Appearance: Fine, branching cracks — usually in weld seams or stressed areas
Hazards:
- Brittle cracking — no deformation — sudden failure
- Risk of explosion at high pressure
Diagnosis:
- Microscopic inspection — Intergranular cracks
- EDS analysis: presence of Na or K at the crack site — ICP analysis: high alkali concentration in water

Corrosion in the boiler - there is corrosion after descaling
Accurate Detection Methods — Advanced Laboratory Analysis
Advanced laboratory methods are essential for accurate detection of the type of deposit or corrosion. Here we introduce 3 main methods:
1. XRD (X-Ray Diffraction) — Identification of crystalline compounds
- Application :Accurate identification of deposit mineral compounds (CaCO₃, CaSO₄, SiO₂, Fe₂O₃)
- Advantage : Non-destructive — Fast — Accurate
Output : Diffraction spectrum — with distinct peaks for each compound
2. SEM-EDS (Scanning Electron Microscopy + Energy Dispersive X-Ray Spectroscopy)
Application:
- SEM: Imaging of surface morphology (cavity, crack, deposit layer)
- EDS: Local elemental analysis (identification of Ca, S, Si, Fe, O, Cl, Na, etc.)
Advantage: Image combination + chemical composition — ideal for detecting sub-deposit corrosion and cracks
3. ICP-OES (Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectrometry)
- Application:Quantitative analysis of elements in feed water or wash solution (concentration of Ca, Mg, Si, Fe, Na, Cl, etc.)
- Advantage: High sensitivity — ppm to ppb measurement
Use in diagnosis:
- High Si concentration → silica warning
- High Fe concentration → corrosion warning
- High Na/Cl concentration → alkaline or sub-precipitation corrosion warning
✅Laboratory summary:
- XRD → to identify the type of deposit
- SEM-EDS → to identify the corrosion mechanism and local composition
- ICP → to identify the concentration of elements in water and solutions
Quick diagnosis checklist — What is the type of deposit or corrosion?
Before sending the sample to the laboratory, make an initial guess with this quick checklist:
Feature | Calcium carbonate | Calcium sulfate | Silica | Iron oxide | Oxygen corrosion | Subsoil corrosion | Alkali corrosion |
Color | White/Gray | White/Yellow | Glass/Matte | Matte | Red/Black | - | - |
Hardness | Fragile | Very hard | Very hard | powdery | - | - | - |
Solubility in HCl | ✅ With bubbles | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | - | - | - |
Place of formation | Pipes, drums | Pipes, drums | Pipes, drums | Pipes, drums | Feeding line, drum | Under the sediment | Welds, stress areas |
Operational signs | Temperature increase | Temperature increase | Temperature increase | Increased TDS | Sudden leak | Leakage under sediment | Crack in the weld |
Practical Solution: Abrizan Industrial Research Company — Accurate Diagnosis and Specialized Treatment
If you are looking for accurate diagnosis and specialized treatment for scale or corrosion in your boiler, Abrizan Industrial Research Company, with its well-equipped laboratory and expert technical team, is ready to be by your side.
Specialized laboratory — Accurate diagnosis with XRD, SEM, ICP
- Send a sample of sediment or corroded metal
- Complete analysis in less than 72 hours
- Specialized report with a proposal for a specific formulation
Mitreh brand specialized products — Treatment of any type of sediment and corrosion
- Special anti-sedimentation and anti-corrosion for high-pressure boilers
- Special anti-sedimentation and anti-corrosion for medium and low pressure boilers
- Special anti-sedimentation for the vapor phase of boilers
- Special anti-sedimentation and anti-corrosion for hot and hot water boilers
- Types of oxygen scavengers: To prevent oxygen corrosion — Removal of dissolved O₂
- Special vector sedimentation to remove corrosion products
- Types of neutralizers after sediment removal
- And ...
Field chemical washing services
- Performing washing with a specific formulation — Under laboratory supervision
- Pre- and post-washing report — With ICP analysis of washing water
Free specialized consultation
- Send photos or operational data → Free pre-diagnosis
- Send a free sample + manual
Request free technical advice and analysis and direct contact with a sales expert


✅ Final Conclusion:
Accurately diagnosing the type of scale or corrosion in your boiler is the first and most important step to proper treatment. Using advanced laboratory methods (XRD, SEM, ICP) will help you choose the best chemical solution without guesswork and avoid additional costs and safety risks.
Abrizan Industrial Research Company with the Mitreh brand, relying on a specialized laboratory, formulated products and a professional executive team, is ready to increase the efficiency of your boiler, reduce operating costs and increase the life of your equipment by up to 2 times.
share :













Submit your opinion
Your email address will not be published.