Types of cooling towers in terms of airflow | natural, mechanical, forced, induced, mixed

Introduction: Why is air flow in a cooling tower critical?
A cooling tower is one of the most important industrial equipment in the world today. From power plants to petrochemical plants, food factories and building air conditioning systems, they all depend on this system based on the evaporative cooling process.

Cooling towers are the source of cooling water in every industry. They maintain the operating temperature of machinery, absorb heat from chillers, boilers and furnaces and reduce equipment wear and tear.
But the type of airflow in a cooling tower determines its efficiency, energy consumption, maintenance requirements and even the type of chemicals needed for cleaning and protection.
In this article, you will learn about the 5 main types of cooling towers in terms of airflow and understand:
✅ How each one works
✅In which industries are they used
✅What chemical challenges (sediment, corrosion, biofilm) do they face
✅What specialized chemical maintenance solutions are available for each
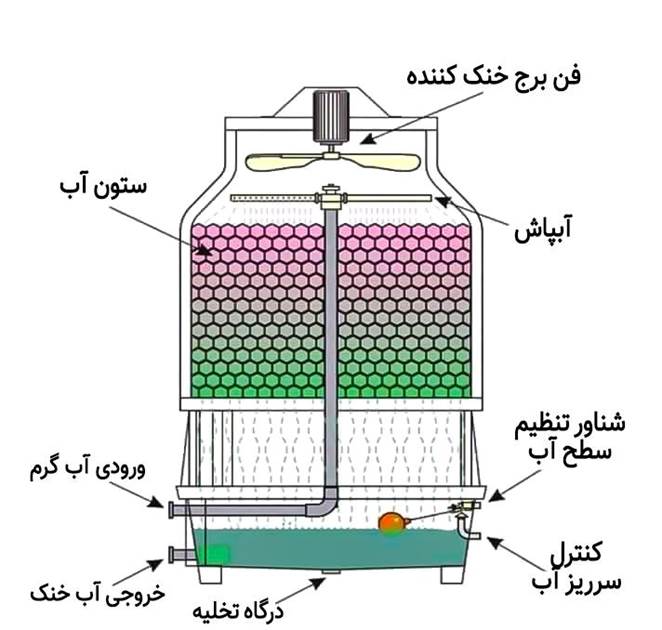
What is a cooling tower and how does it work?
A cooling tower is an advanced system with a cooling mechanism that converts available heat into cool water. This process, called evaporative cooling, saves a significant amount of water while preventing water waste.

Climate cycle in cooling tower
Simple formula for operation:
Hot water → Entering the tower → Contact with air → Evaporation section (heat transfer) → Cold water → Return to the system
Cooling tower key point:
The speed and quality of this process depends entirely on the way the air flows in the tower, and this is where the following divisions make sense.
Introducing 5 types of cooling towers in terms of air flow
1. Natural Draft Cooling Tower

Airflow mechanism:No fan — air flow is created only by the temperature difference and the height of the tower (chimney effect).
Application:Thermal and nuclear power plants — where the volume of cooling water is very high.
Advantage:
- Zero energy consumption for the fan
- Long life — very robust design
Chemical challenge:
- Very long water cycle → heavy calcium carbonate deposition
- Requires strong sedimentation vectors and regular washing cycles
2. Mechanical Draft Cooling Tower
This category is itself divided into two subcategories:
Forced Draft Cooling Tower
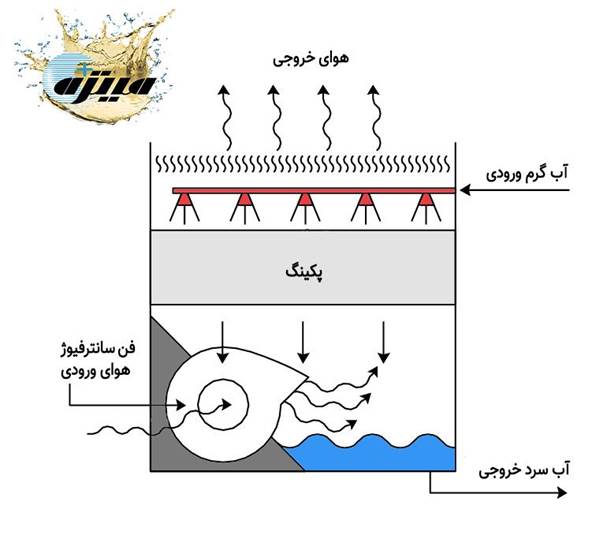
Cooling tower with fan at the bottom
Airflow mechanism:Fan at the bottom of the tower — blows air into the system.
Application:Industries with limited space — where tall towers cannot be used.
Advantage:
- More precise control of air flow
- Suitable for confined environments
Chemical challenge:
- Steam accumulation at the top of the tower → corrosion of metals in wet areas
- Requires anti-corrosion with a strong protective coating
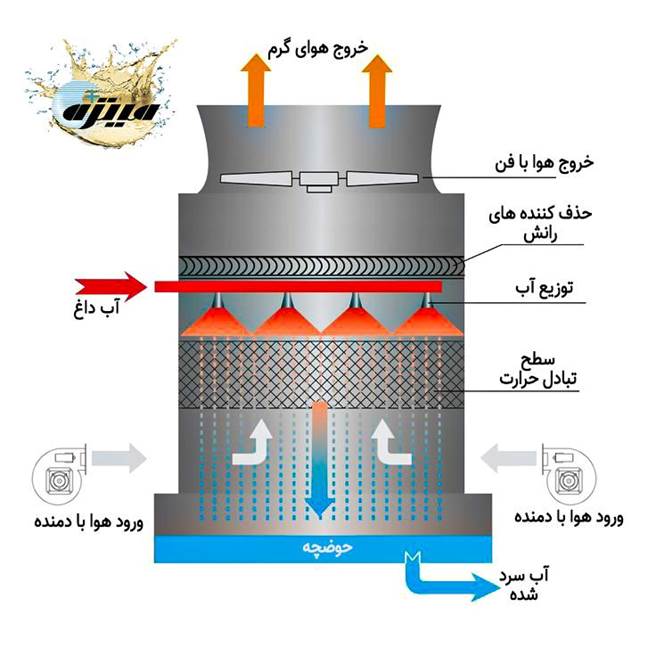
Induced Draft Cooling Tower
Cooling tower with fan on top
Airflow mechanism:Fan at the top of the tower — draws air from the inside out.
Application:Most common type in industries — from petrochemicals to construction facilities.
Advantage:
- Even air distribution
- Reduced risk of freezing in cold areas
Chemical challenge:
- Deposition on fins and draft → Reduced air flow
- Biofilm growth in wet area → Odor and subsoil corrosion
3. Hybrid Draft Cooling Tower
Combined cooling tower
Airflow mechanism:Combination of natural + mechanical — depending on environmental conditions, the system switches between two modes.
Application:Advanced industries — where saving water and energy at the same time is important.
Advantage:
- Optimization of water and electricity consumption
- High flexibility in different climatic conditions
Chemical challenge:
- System complexity → Need for multi-layer chemical monitoring
- Temperature and flow variations → Irregular fouling
Why is chemical maintenance of any type of cooling tower necessary?
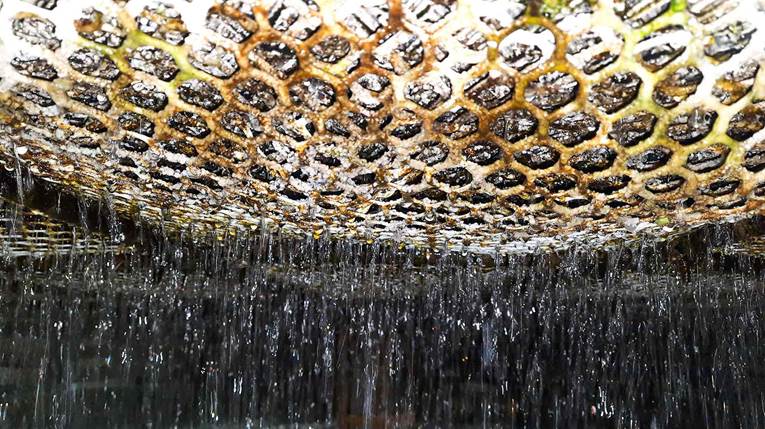

Deposits inside the cooling tower
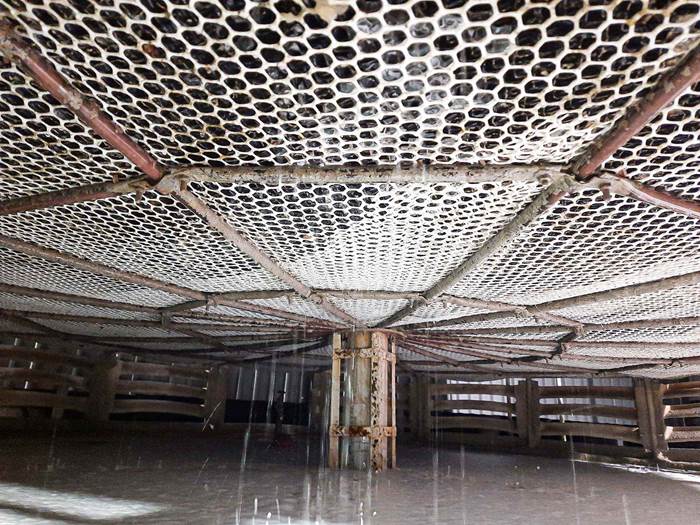

Inside the cooling tower after sediment removal

Sample of sediments inside the cooling tower
The design of cooling tower components requires precise engineering knowledge, and with the advancement of the industry, the quality of this equipment has reached the highest level.
But without regular chemical maintenance, even the best cooling tower in the world:
- Lose efficiency
- Increases energy consumption
- Reduces the life of connected equipment
- Can lead to costly production line downtime
Specialized Cooling Tower Chemical Maintenance Solutions
Cooling tower type | The main challenge | Recommended washing cycle |
Natural flow | Intense carbonate sedimentation | Every 6-12 months |
Forced flow | Corrosion in the steam zone | Every 12 months + permanent anti-corrosion |
Induced current | Biofilm + fin deposits | Every 6-12 months |
Compound flow | Multiple + temperature changes | Every 12 months + weekly monitoring |
Frequently Asked Questions
1: Can the cooling tower be washed without stopping the production line?
Yes! Abrizan Company performs chemical washing without stopping the production line with specialized methods and bypass systems — even in petrochemical plants and power plants.
2: Why is pure water also dangerous?
Ultrapure water (such as distilled water) causes severe corrosion of metals due to the lack of protective ions. For these cases, we use Mitreh anti-corrosion.
3: When should chemical washing be performed?
It is better not to wait for signs of damage. Our recommendation:
- Heavy industries: every 6-12 months
- Food industries: every 6 months
- Construction facilities: every 12 months
Free expert consultation with Abrizan
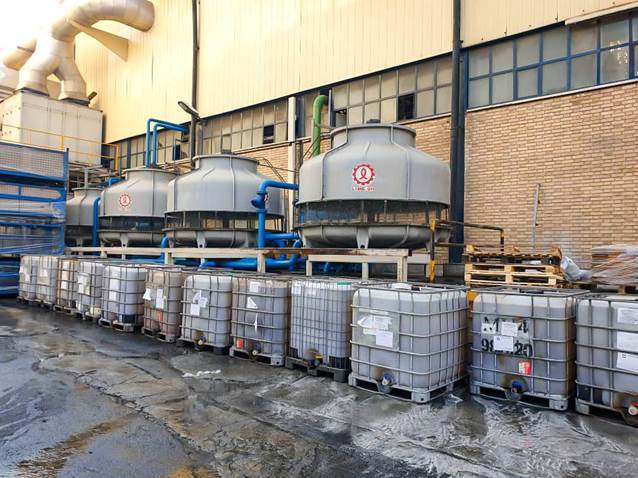

Cooling Tower Sediment Removal Project Implementation by Abrizan Company
If you want to:
- Identify your cooling tower type
- Learn the best chemical maintenance method
- Receive a periodic cleaning schedule for your equipment
Contact us now:
Request a free consultation:
You can contact us in the contact section. Or send us a message via the contact form.
✅Abrizan Special Services:
- Free testing of your cooling tower water sample
- Sending a diagnosis report + Mitreh product suggestion
Planning cleaning without stopping the production line
share :












Submit your opinion
Your email address will not be published.